TECHNOLOGIES
Water Treatment Process
Advanced membrane bioreactor method
By introducing partial modification of the removal mechanism in the A2O method, it removes organic matter, nitrogen and phosphorus caused by nitrification, denitrification and excessive phosphorus in a bioreactor tank composed of anoxic, anaerobic, aerobic and internal transfer tanks. It is a sewage treatment technology that separates solid and liquid and removes coliform bacillus by installing an immersed hollow fiber membrane in an aerobic tank instead of a settling tank. This separation membrane method that uses a sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) in an aerobic tank to clean utilizing natural flow when the hollow fiber membrane is contaminated.
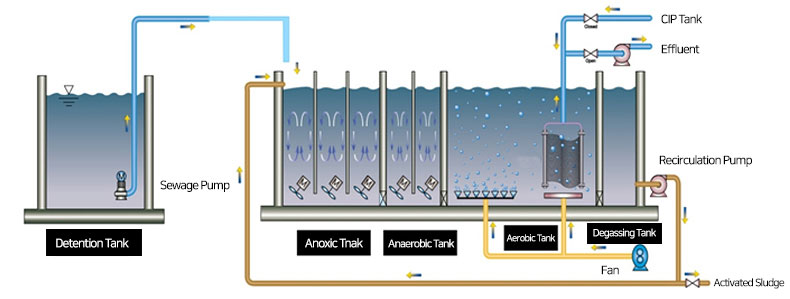
Configuration and function
| Configuration | Function |
|---|---|
| Anoxic tank | NO3-N in the internal returned water is reduced by denitrifying microorganisms and converted to N2Gas to remove nitrogen (N) |
| Anaerobic tank | In the anaerobic state, organic matter is absorbed into the cells of phosphorus-removing microorganisms and phosphorus is re-released to obtain the required energy. |
| Aerobic tank |
|
| Degassing tank | Internal return to anoxic tank |
Performance
- Excellent ability to cope with temperature and load fluctuations by maintaining high MLSS
- As there is no final settling pond, there is little plottage and facility arrangement is smooth.
- Separated filtration and disinfection facilities are unnecessary as stable treatment water quality is secured by separating solids using membranes.
| Water quality assurance | BOD | 5 ㎎/ℓ |
| SS | 5 ㎎/ℓ | |
| T-N | 20 ㎎/ℓ | |
| T-P | 2 ㎎/ℓ | |
| Total coliform bacillus | Non-detection |